Factors That Affect the Duration of Sunburns. This comprehensive guide provides information about sunburn duration as well as factors that can influence them. It provides tips on preventing, managing, and seeking medical attention, as well as how to protect your skin against the sun’s harmful rays and ensure a rapid recovery from sunburns.
Introduction:
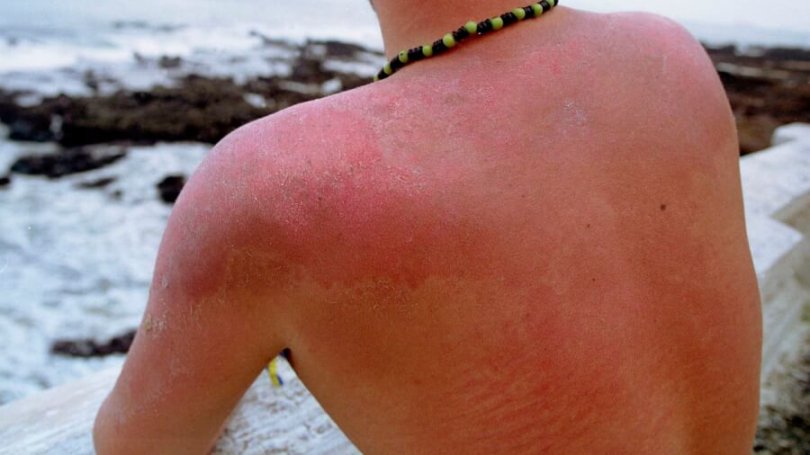
Sunburns can be uncomfortable and sometimes painful if you spend too much time in the sun without adequate protection. It can be painful and uncomfortable to suffer from a sunburn, but its effects can last for much longer.
Duration of Sunburns
It is possible for sunburns to last between 2-3 days depending on their severity. Mild sunburns, characterized by redness, pain, and swelling, usually last between two and three weeks. Moderate sunburns, which are characterized by redness, swelling, and pain, can last up to one week. A severe sunburn can cause blistering, pain, and blistering for approximately two weeks.
Factors That Affect the Duration of Sunburns
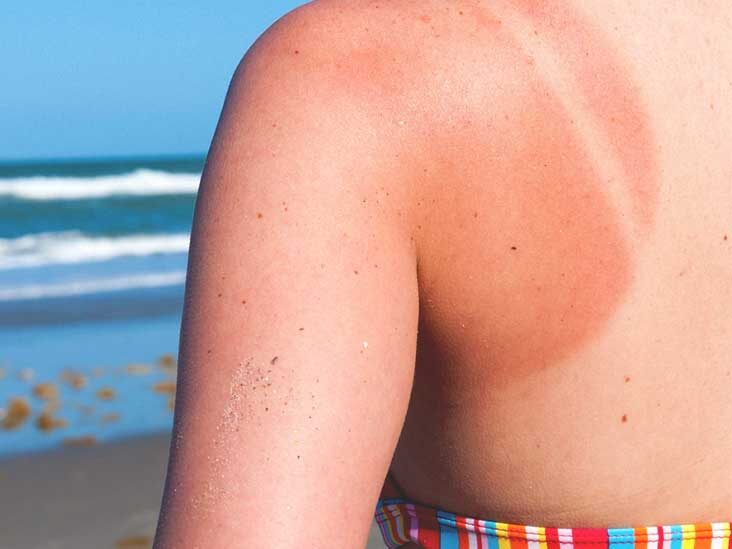

It is important to note that there are a number of factors that can influence the duration of sunburn, including:
- Skin Type: Fair-skinned individuals are more likely to suffer from sunburns and may experience more severe symptoms.
- Age: We lose the ability to repair our skin as we age, leading to a longer duration of sunburns.
- Medications: Antihistamines and blood pressure medication may increase the risk of sunburn and lengthen the duration of the burn.
- Dehydration: Dehydration can prolong the healing process of sunburn and can also make the symptoms more severe.
- The severity of the burn: There is a direct link between the severity of a Sunburn and the length of time it takes to heal. Severe sunburns may cause long-term damage to the skin due to the long healing time.
Managing and Preventing Sunburns
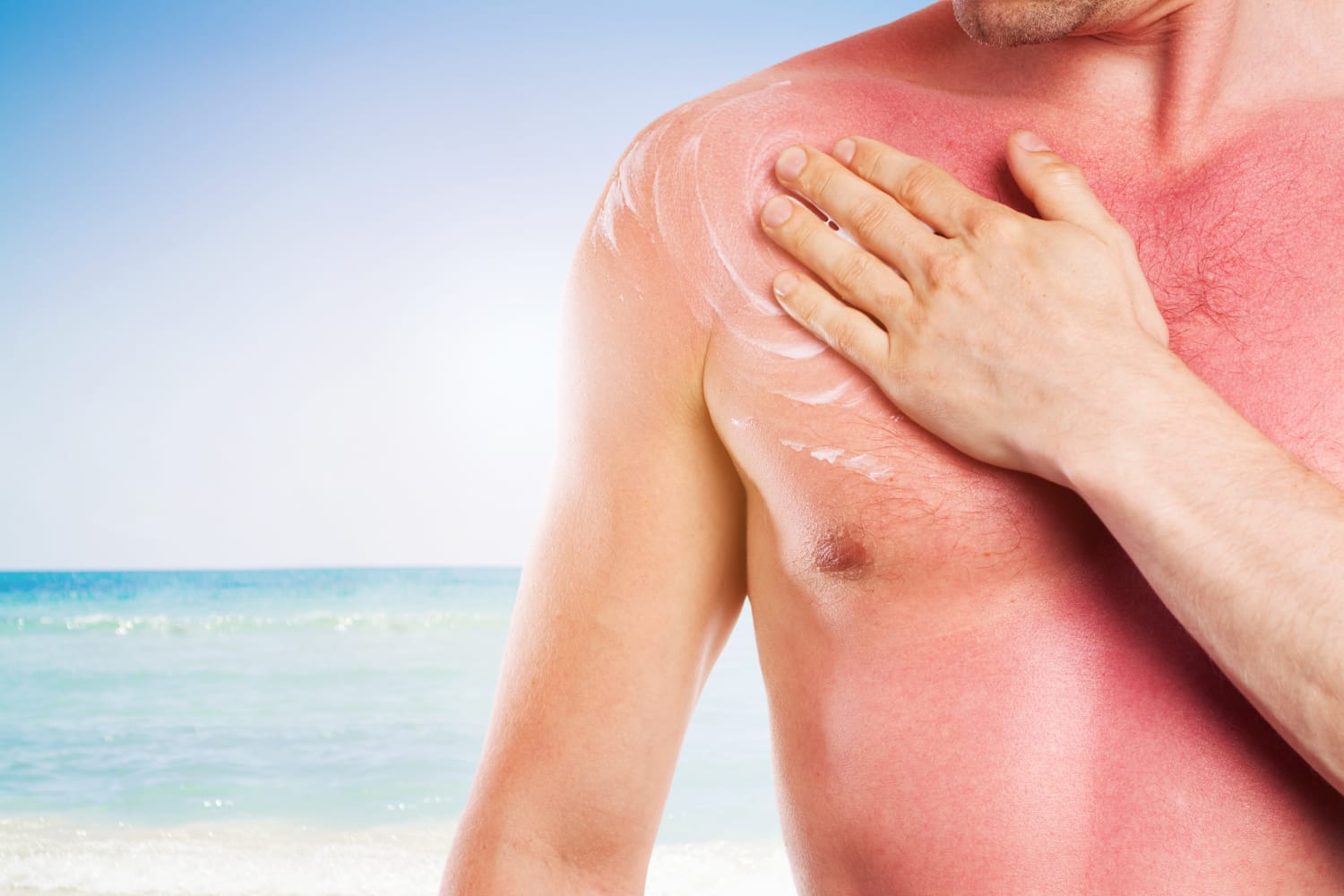

A sunburn can last anywhere from a few minutes to a number of days. The following steps will help you manage and prevent sunburn:
- Sunscreen: You can prevent sunburns by using sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. Reapply sunscreen every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
- Clothing: Sunburn can also be prevented by wearing protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and wide-brimmed hats.
- Timing: Refrain from prolonged exposure to the sun during the middle of the day when the sun’s rays are at their strongest.
- Hydration: To aid in the healing process, drink a sufficient amount of water to prevent dehydration. To aid in the healing process, drink a sufficient amount of water to prevent dehydration.
- Seek shade: Sun exposure during the middle of the day when the sun’s rays are strongest should be avoided.
- Check the UV index: Pay attention to the UV index before going outside and take the necessary precautions.
FAQs
1. How long do sunburns last?
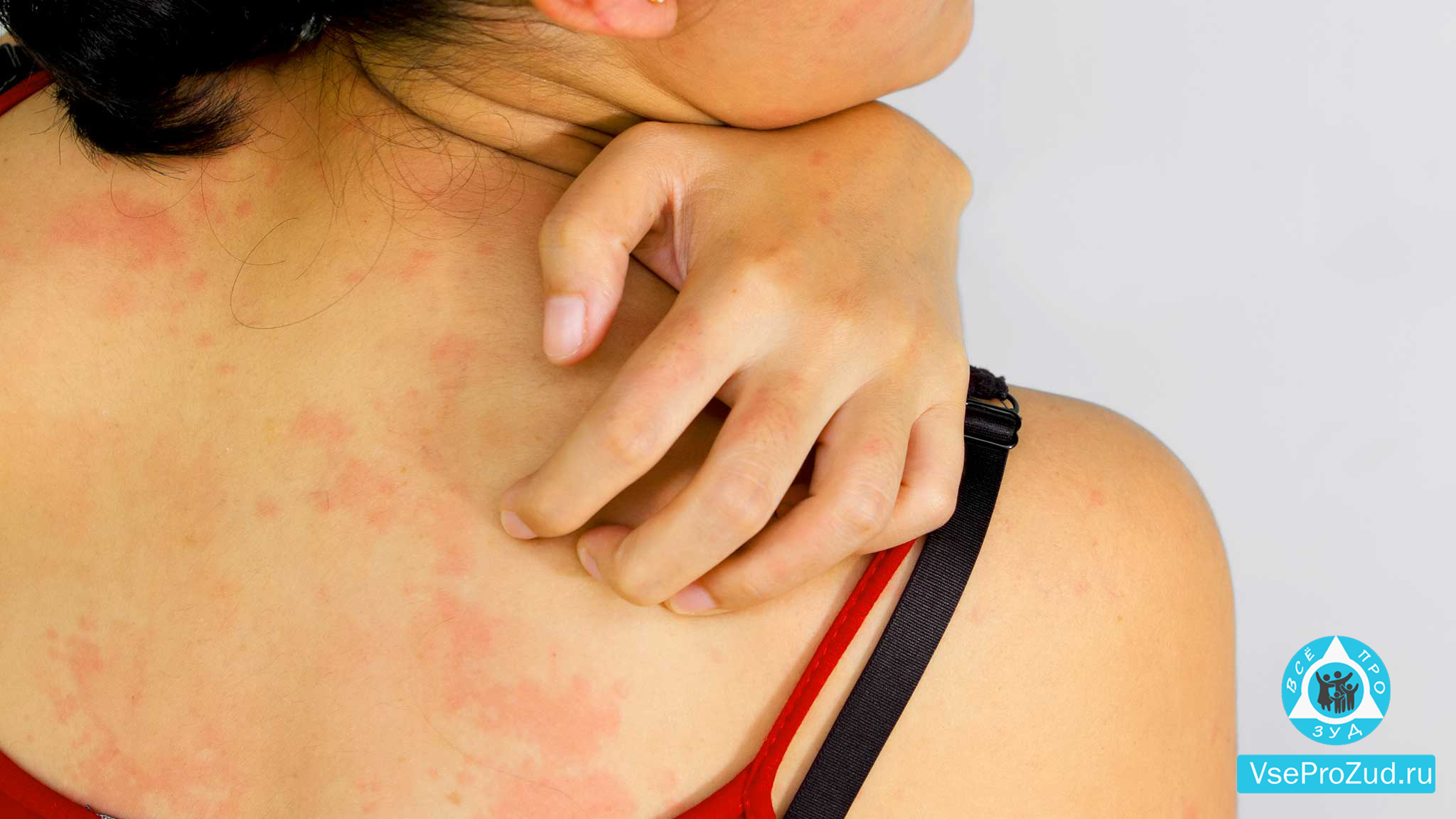
Sunburn duration varies according to a number of factors, including the severity of the burn, the amount of sun exposure, and the skin type of the individual. In general, mild sunburns will last for a few days and should begin to heal within a week. Moderate sunburns may last up to a week or more and may cause peeling or flaking of the skin. Several weeks may pass after a severe sunburn, which can result in blistering, swelling, and fever.
2. How can I manage sunburns?
The key to managing sunburns is to soothe the skin and encourage healing. Take a cool shower or bath, apply aloe vera gel or a lotion, take over-the-counter pain medication, and stay hydrated.
3. What are the potential complications of a sunburn?
There are a variety of potential complications associated with sunburns, including dehydration, heat exhaustion, heat stroke, and peeling. Sun poisoning can also be caused by severe sunburns, resulting in symptoms such as fever, chills, nausea, and dizziness. In addition to premature aging of the skin, wrinkles, age spots, and skin cancers, long-term complications can occur as a result of sun exposure.
The use of sunscreen and the wearing of protective clothing are important methods for protecting your skin from the sun, especially during peak sun hours.
4. Is it possible to tan without getting a sunburn?
You can tan without getting sunburned, as tanning is one of the body’s natural defense mechanisms to protect the skin against further damage caused by UV rays. UV rays cause the skin cells called melanocytes to produce more melanin, which is the pigment that gives the skin its color. This is what causes the skin to darken and result in tans.
Conclusion:
Sunburn is a commonly occurring skin condition caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun. Sunburns may last for up to two weeks or more depending on the severity of the burn and the individual’s skin type, with mild sunburns lasting 2-3 days, moderate sunburns lasting up to a week, and severe sunburns lasting up to two weeks.
Stay hydrated and avoid prolonged sun exposure during the middle of the day. Wear protective clothing and wear protective clothing when exposed to the sun for long periods during the day.